“You’ve just finished triage on an urgent decision about the current cash crunch and a simultaneous huge opportunity. You must act decisively and within days, or the opportunity will be lost, and the business could be set back years—if you can stay liquid at all. You realize this decision requires your full attention and the best tools you can muster. What’s next?”
“Bad decisions come from bad processes. A clear decision-making framework ensures you assess options effectively and act with confidence, without missing crucial details.”
Better Decisions, Better Lives - Decision Education Foundation
“In this post, we’ll explore three essential decision-making frameworks—the D.E.F. Decision Chain, the OODA Loop for rapid decisions, and the PDCA Cycle for continuous improvement. By the end, you’ll have the mental tools to help you tackle high-stakes choices with confidence and precision.”
The D.E.F. Decision Chain
“One powerful framework to improve decision quality is the Decision Education Foundation (D.E.F.) Decision Chain. Imagine this scenario: You’re tasked with choosing between several business strategies. Each option seems viable, but you can’t shake the feeling that you’re missing something. This is where the Decision Chain comes in, guiding you through each critical step to ensure nothing gets overlooked.”
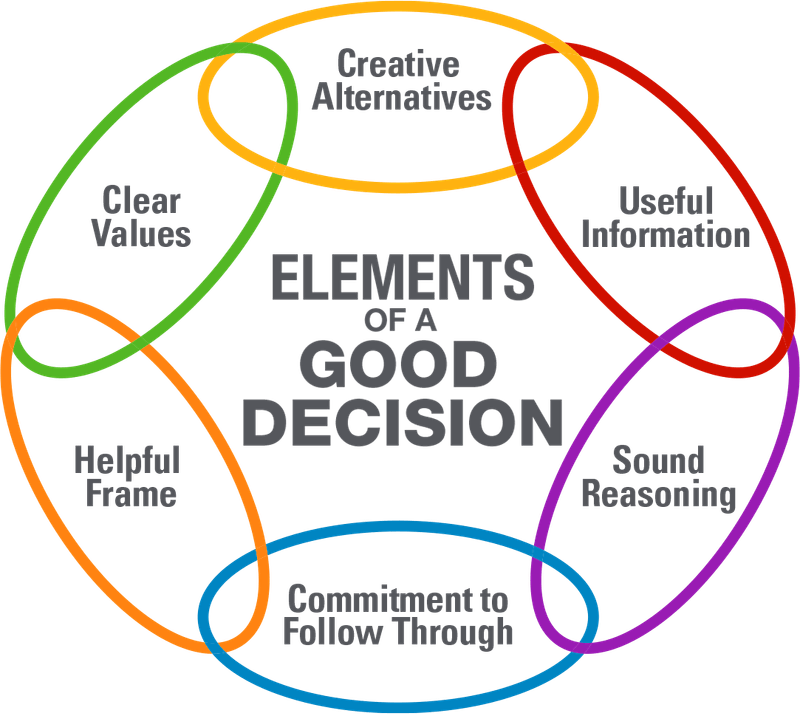
The Decision Chain focuses on strengthening each link in the decision process, ensuring clarity and robustness at every step. It consists of five key components:
Clarity of Values: Understand what truly matters, why it's important, and how to ensure it aligns with those core values.
Creative Alternatives: Get creative. Generate a broad range of potential solutions, avoiding the trap of binary thinking. Mix and match ideas.
Relevant Information: Focus only on the data that impacts the decision and filter out noise.
Sound Reasoning: Apply logical and critical thinking to evaluate the alternatives objectively.
Commitment to Follow-Through: Once the decision is made, ensure there’s a plan in place to execute it effectively.
“The strength of the D.E.F. Decision Chain lies in its systematic approach to making sure that each component of the decision is thoughtfully addressed. If you miss just one link—such as failing to explore creative alternatives—you could end up with a limited and shortsighted choice.”
The Decision Chain is only as strong as its weakest link. - Decision Education Foundation
The OODA Loop for Rapid Decision-Making
“In fast-moving environments, whether in business or personal life, decisions need to be made quickly and iteratively. The OODA Loop, developed by military strategist John Boyd, is a powerful framework for rapid decision-making. Created for fighter pilots in high-pressure situations, this model is now widely used in various fields, from business to emergency response.”
The OODA Loop consists of four continuous steps:
Observe: Collect information from your surroundings. In a business context, this could mean gathering market data, customer feedback, or analyzing competitor behavior.
Orient: Make sense of the situation. Use your background, experience, and intuition to understand the context of your decision.
Decide: Based on the observations and orientation, choose a course of action. You may not have perfect information, but the key is to make a decision swiftly.
Act: Implement your decision immediately and observe the results, which feeds back into the cycle.
The beauty of the OODA Loop lies in its adaptability. You are constantly gathering new data, reorienting, and adjusting your decisions. It’s not about making one perfect decision but rather a series of smaller, more agile decisions that adjust to the situation as it evolves.
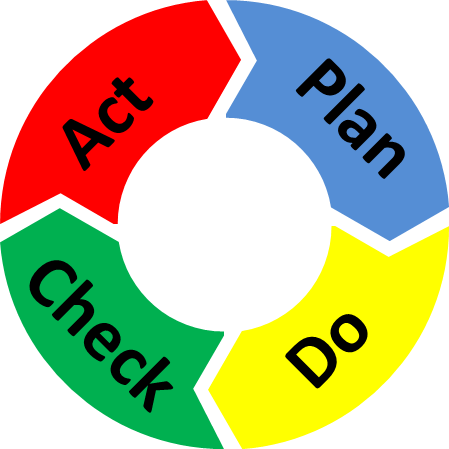
The Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA) Cycle
“When it comes to continuous improvement and refining processes, the Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA) Cycle, developed by W. Edwards Deming, is one of the most widely used frameworks. Originally designed for quality control in manufacturing, it has since been adopted across industries for iterative problem-solving.”
The PDCA Cycle consists of four stages:
Plan: Identify a problem or goal and create a detailed plan to address it. This involves analyzing the current situation, defining objectives, and outlining the steps needed to achieve the desired outcome.
Do: Implement the plan on a small scale to test its effectiveness. This stage is about execution but in a controlled, low-risk manner to gather insights.
Check: Review the results of the test and compare them against the expected outcomes. Did the plan work as intended? If not, what went wrong? This stage is where lessons are learned, and adjustments are considered.
Act: Based on the insights gained in the Check phase, either scale the plan for broader implementation or go back through the cycle to make further refinements. The key here is to take what you’ve learned and act on it for continuous improvement.
Key Takeaways from Other Frameworks:
S.M.A.R.T. Goals Framework - “The S.M.A.R.T. framework ensures that decisions and goals are well-defined and actionable. By being Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound, it helps align decisions with clear outcomes and realistic timelines, making it ideal for goal-setting and project management.”
Society of Decision Professionals (SDP) - Value-focused thinking shifts the focus from reactive decision-making to proactive decision-making. Clarifying values and objectives upfront ensures decisions align with long-term goals, making it highly effective for strategic decision-making.
The Cynefin Framework helps categorize problems into distinct domains: Simple, Complicated, Complex, and Chaotic. This allows you to adapt your approach depending on the nature of the problem, making it a valuable tool for navigating uncertain or volatile environments.
Six Thinking Hats
The Six Thinking Hats framework encourages decision-makers to see a problem from multiple perspectives. Using various thinking modes like logic, emotion, and creativity fosters balanced, innovative solutions, especially in groups that value diverse viewpoints.
The Weighted Decision Matrix or Pros and Cons framework, also called a “Rate and Weight” table, offers a structured way to compare multiple options by assigning weights to various factors. This method simplifies decision-making by breaking down complex choices into clear trade-offs, making it practical for everyday decisions.
Note: A great decision process leads to great results. Choosing the right framework for the situation is essential to success. Whether it’s rapid action with the OODA Loop, continuous improvement with PDCA, or strategic alignment with Value-Focused Thinking, the framework shapes the decision and the outcome.
“The right decision-making framework can transform how you approach complex choices. "Each framework has strengths; the key is knowing when to use them."
Whether you’re facing high-stakes business decisions or daily challenges, having a solid process ensures you don’t overlook critical steps.”
These frameworks equip you with the mental tools to tackle decisions with clarity, confidence, and precision. The next time you face a tough decision, take a moment to choose the framework that will guide you to the best outcome.
That's My Perspective